Editorial
Volume 1 Issue 3 - 2017
Managing Complex R&D Projects- Strategies from Project Management Perspectives
Manoshi Complex, Ghansoli, Navi Mumbai -400701, India
*Corresponding Author: Prashant Pandya, Manoshi Complex, Ghansoli, Navi Mumbai -400701, India. Tel: +91 9967017172; Email id: drpandya18@gmail.com
Received: May 23, 2017; Published: May 30, 2017
Abstract
Managing a complex R&D projects require exceptional techniques and different mentality. Complex projects are a higher-order management activity and have to be treated differently and resourced for that reason. There is high level of uncertainty regarding goals and/or implementation.
A comprehensive literature review on the changing roles of a project management in managing complex projects is the theoretical foundation of the paper. The paper concludes that there are specific project management skill sets needed, and that the skills comes from knowledge gained from previous projects. If there are any mismatch of skills and project complexity could lead to the failure of these projects.
Keywords: Complex projects; Project Management; Perspectives; Skill set
Introduction
Globalization and healthy competition have played a key role in driving the industry to the limits. The industry is trying to pace up with progressively growing demands, varying needs and objectives [1-2].
In the twenty-first century, business processes have become more complex; i.e., greater interconnected, interdependent, and interrelated than ever earlier than. In addition, businesses today are rejecting conventional management systems to create complicated organizational groups made out of alliances with strategic providers, networks of clients, and partnerships with key political groups. Due to this, upcoming projects are becoming more complex. This complex and dynamic requirements call for efficient project management. Traditional strategies won't work here. Complex projects require additional efforts and thinking beyond the ordinary green field sites. On international projects it could be the cultural differences, knowledge of local people and work situations that that would cause them to complex [3-6].
Pattern of Complexity
Definition
Complex projects are characterized by a degree of disarray, instability, evolving decision-making, non-linear processes, iterative planning and design, uncertainty, irregularity, and randomness. It is difficult to use Standard practices achieve project success due to dynamic interactions between project factors.
Definition
Complex projects are characterized by a degree of disarray, instability, evolving decision-making, non-linear processes, iterative planning and design, uncertainty, irregularity, and randomness. It is difficult to use Standard practices achieve project success due to dynamic interactions between project factors.
Some of the causes of project complexity include:
- Details – Range of factors and interfaces
- Ambiguity – Absence of familiarity with circumstance and causality
- Uncertainty – Powerlessness to pre-assess activities
- Unpredictability – The inability to recognize what will happen
- Dynamics – Fast rate of progress
- Social structure – Numbers and types of associations
- Interrelationships – Numerous interdependencies and interconnections exist
| Traditional Projects | Complex Projects |
| • It can be managed by Standard practices. – Design – Funding – Contracting • Static in nature • High level of closeness to earlier projects creates certainty |
• Difficult to use Standard practice – Design – Funding – Contracting • Dynamic – need continuous monitoring • Higher level of uncertainty regarding objectives |
Source: Jennifer Shane, Kelly Strong (2012), Guidebook: Project Management Strategies for Complex.
Table 1: Comparison of project characteristics.
Table 1: Comparison of project characteristics.
The concept of complexity is being used as an umbrella term associated with difficulty and inter-connectedness. Complexity is usually also associated with variety, so that complex systems consist of the interconnection and interdependence of distinct parts. The five dimensions of complexity are [1,7].
- Cost: Brief scope and associated cost. Cost considers project estimates, contingencies, uncertainty, project-related costs, and project cost drivers and constraints
- Schedule: Time needed to complete project. It considers associated risks, defined milestones, and resources availability.
- Technical: It includes technical capabilities considering scope of the project.
- Context: It includes stakeholder involvement, regulatory requirements, Local factors and project specific factors.
- Finance: It includes milestone payment and scope of work.
Project Management
Project Management is about the management of risk and uncertainty in delivering project outcomes; especially the risk of abrupt and irreversible emergent effects that escalate rapidly. In order to deal with these new complexities, successful organisations are shifting from centralised power and decision making structures to a distributed, shared leadership model, which involves a shift from ‘power over’ to ‘power with’. Effective project management and the implementation of a systems approach are key elements in a strategy designed to ensure successful achievement of a project's objectives [1,3,5,6].
Project Management is about the management of risk and uncertainty in delivering project outcomes; especially the risk of abrupt and irreversible emergent effects that escalate rapidly. In order to deal with these new complexities, successful organisations are shifting from centralised power and decision making structures to a distributed, shared leadership model, which involves a shift from ‘power over’ to ‘power with’. Effective project management and the implementation of a systems approach are key elements in a strategy designed to ensure successful achievement of a project's objectives [1,3,5,6].
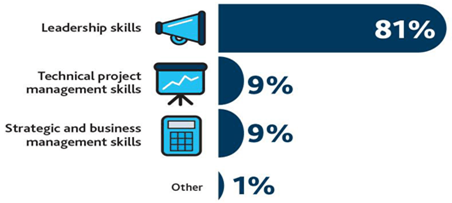
Skills needed to manage highly complex projects:
Discussion
Project complexity is viewed differently by different people Technically complex projects are important for organizations but it is important to have specialized team to handle the same. Association with such types of project is exceptionally dangerous without proper team and prior experience else it will lead to disasters.
There are various ways to deal with the complex projects:
- Good Governance
- Improving project preparation
- Improving communication
- Hire experienced resources
- Listen to your experts
- Quality control at each steps
- Using knowledge management tools
- Manage integration effectively
Managing complex projects needs careful planning and exact estimation before start of the project in terms of manpower/ resources and agreed timelines prior to starting the project execution. Project plan is important and it should mention all the requirements and should clearly define the goals of the project. It is crucial to prepare project plan at the start of project & must be shared with all the stakeholders involved in the project so that everyone get a clear idea about project deliverables and deadlines. Risk mitigation plan is also needed which help to manage project effectively. It is important to identify every risk that is involved in the project, the consequences and its impact must be clearly outlined [2,5,7].
Conclusion
Effective project management is crucial for the management of complex project. It is important that project managers should adopt both a system and pluralistic approach with multi ways of thinking and create new methods to suit their projects and use skill for the successful conduct of project.
It was observed that, Project success is dependent on several factors like project planning, Stakeholder management, technical capability, organizational structure, monitoring and controlling, team expertise, project communication, leadership style, strategic decision, training and development and risk management during execution of project.
Recommendations
- Committed leadership is crucial for managing complex project.
- Different types of projects need different types of project managers. Qualities of project manager play important role in complex project. PM with open mind and thinking outside the box with special skill to achieve outcome is important.
- Careful planning at the start of project is needed as project generally fails because crucial interrelationships where not taken into consideration or there is issue in understanding.
- Robust quality framework is essential to manage rising follow-up costs.
- It is also critical to conduct enterprise analysis at the start of project.
References
- Remington K and Crawford L. (2004). “Illusions of Control: Philosophical Foundations for Project Management”. IRNOP VI Conference, Turku, Finland August (2004): 25-27.
- Baccarini D. “The concept of project complexity a review”. International Journal of Project Management 14.4 (1996): 201-204.
- Glen Mouchi. “The skill sets required for managing complex construction projects”. Business education and accreditation 3.1 (2011): 89-100.
- Crawford I. “Profiling the competent project manager”. Proceedings of PMI research conference. Newtown Square, PA: Project Management Institute (2000).
- Hartman F and Ashrafi RA. “Project management in the information systems and information technology industries”. Project Management Journal 33.3 (2002): 5-15.
- Wildemann H. “Komplexität: Vermeiden oder beherrschen lernen”. In Harvard Business Manager 6 (1999): 30-42.
- Jennifer Shane and Kelly Strong. Guidebook: Project Management Strategies for Complex Projects National Academy of Sciences (2012).
Citation:
Prashant Pandya. “Managing Complex R&D Projects- Strategies from Project Management Perspectives”. Chronicles
of Pharmaceutical Science 1.3 (2017): 114-117.
Copyright: © 2017 Prashant Pandya. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.































 Scientia Ricerca is licensed and content of this site is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Scientia Ricerca is licensed and content of this site is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.